Coolant is an essential component of a vehicle’s engine cooling system. It helps regulate the engine’s temperature and protects it from overheating. However, many car owners are unsure whether coolant can expire or go bad over time.
According to several sources, including a post on Motor Vehicle Maintenance & Repair Stack Exchange, coolant does not expire if it is kept in its original container and is not being used. As long as the container is sealed, there is no practical expiration date for coolant.
This means that car owners can keep their coolant in storage for an extended period without worrying about it going bad.
However, it is important to note that coolant can degrade over time if it is being used in a vehicle’s engine. The coolant can become contaminated with debris and other particles, which can affect its effectiveness.
Additionally, the coolant’s additives can break down, reducing its ability to protect the engine from corrosion and other damage. Therefore, it is recommended that car owners replace their engine coolant every two to five years, depending on the type of coolant they are using.
Understanding Coolant
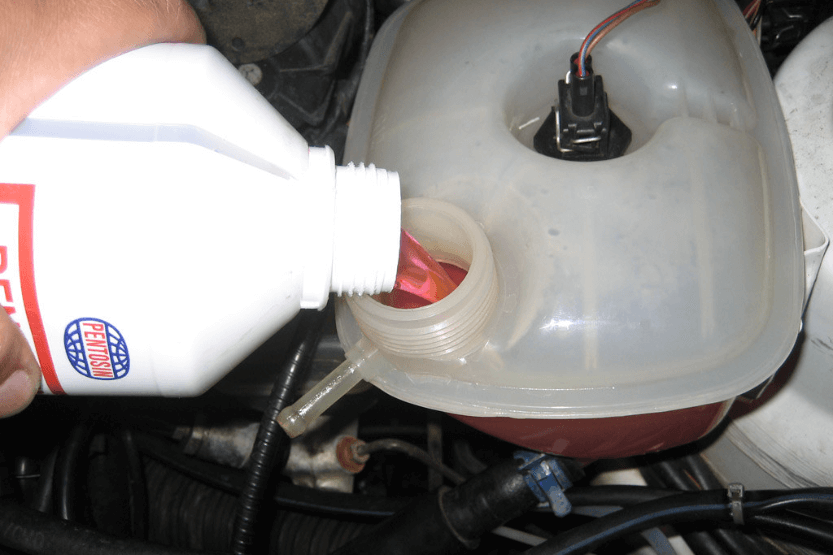
As per Total Energies Egypt, coolant, also known as antifreeze or engine coolant, is a fluid that helps regulate the temperature of the engine by transferring heat away from the engine to the radiator. In this section, we will discuss the components of coolant and the types of coolant available.
Components of Coolant
Coolant is typically made up of three main components: water, ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, and various additives. Water is the primary component of coolant and helps transfer heat away from the engine.
Ethylene glycol and propylene glycol are used to lower the freezing point and raise the boiling point of the coolant. The type of glycol used depends on the manufacturer’s specifications and the climate in which the vehicle operates.
The additives in coolant serve several purposes, including corrosion protection, lubrication of the water pump, and prevention of foaming.
These additives may include silicates, phosphates, and organic acids. The type and amount of additives used depend on the type of coolant and the manufacturer’s specifications.
Types of Coolant
There are several types of coolant available, including traditional green coolant, extended-life coolant, and hybrid organic acid technology (HOAT) coolant.
Traditional green coolant, also known as conventional coolant, is the most common type of coolant and is typically made up of a mixture of ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, water, and additives.
Extended-life coolant, also known as long-life coolant, is designed to last longer than traditional coolant and may be a mix of ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, water, and additives. These coolants typically have a longer service life and may be used for up to 5 years or 150,000 miles.
HOAT coolant is a hybrid of traditional and extended-life coolants and is typically used in newer vehicles. These coolants contain a combination of organic acids and silicates and are designed to provide excellent corrosion protection.
When selecting a coolant, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s specifications and use the correct type of coolant for the vehicle. Using the wrong type of coolant can cause damage to the engine and cooling system.
In summary, coolant is an essential fluid for regulating the temperature of the engine. It is typically made up of water, ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, and various additives.
There are several types of coolant available, including traditional green coolant, extended-life coolant, and HOAT coolant. It is important to use the correct type of coolant for the vehicle and follow the manufacturer’s specifications.
Role of Coolant in Engine
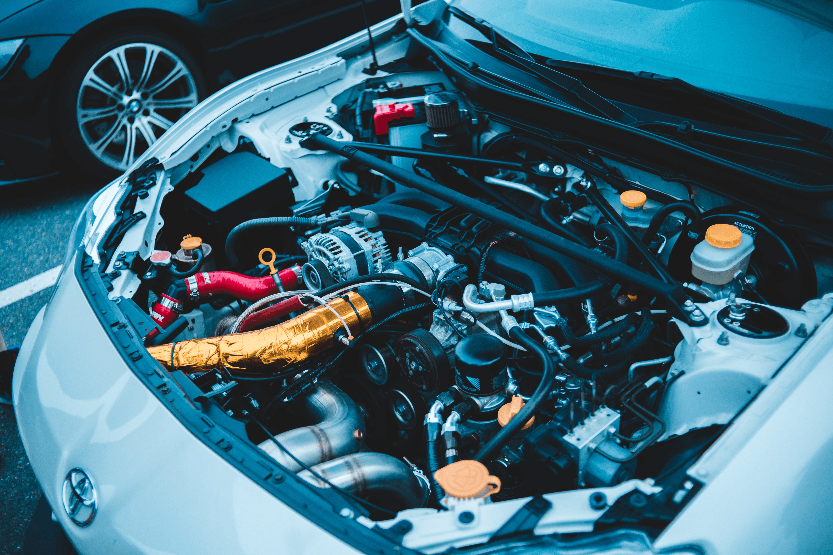
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, plays a crucial role in maintaining the engine’s temperature and preventing it from overheating. The engine generates a lot of heat during operation, and if the temperature is not regulated, it can cause damage to the engine’s components.
The coolant helps to control the engine’s temperature by absorbing heat and transferring it to the radiator, where it is dissipated into the air.
The cooling system consists of several components, including the radiator, thermostat, water pump, and hoses. The coolant flows through these components to remove heat from the engine and transfer it to the radiator. The radiator, in turn, dissipates the heat into the air.
If the engine overheats, it can cause serious damage to the engine’s components, such as the cylinder head gasket, pistons, and bearings. Overheating can also cause the engine to seize, which can be a costly repair.
The boiling point and freezing point of the coolant are also important factors to consider. If the coolant’s boiling point is too low, it can boil and evaporate, leaving the engine without any coolant.
If the coolant’s freezing point is too high, it can freeze and expand, causing damage to the engine’s components.
It is important to note that coolant does not last forever and can expire over time. The shelf life of coolant depends on the type of coolant and can range from two to five years.
It is recommended to check the manufacturer’s guidelines for the specific type of coolant being used. Using expired coolant can lead to reduced performance and can cause damage to the engine.
How to Check Coolant Level
Checking the coolant level in your vehicle is an important part of routine maintenance that can help prevent engine damage. Here are some simple steps to follow:
Identifying Leaks
Before checking the coolant level, it’s important to inspect the engine and radiator for any signs of leaks. Look for wet spots or puddles under the vehicle, as well as any white or green residue around the radiator or hoses. If you notice any leaks, have them repaired before adding more coolant.
Using Test Strips
As per Kia (.com), to check the coolant level, start by making sure the engine is cool. Then, locate the coolant reservoir, which is typically a clear plastic tank near the radiator. The reservoir should have a minimum and maximum fill line marked on it.
Next, use a coolant tester or test strips to check the concentration of the coolant. These strips are available at most auto parts stores and can help you determine if the coolant needs to be flushed and replaced. Simply dip the strip into the coolant and compare the color to the chart on the package.
If the coolant level is low, add a 50/50 mixture of coolant and water until it reaches the maximum fill line. Be sure to use the type of coolant recommended by the manufacturer, as different types of coolant are not always compatible.
Checking the Radiator
In addition to checking the coolant reservoir, it’s also a good idea to check the radiator itself. With the engine cool, remove the radiator cap and check the level of coolant inside. If the level is low, add more coolant until it reaches the top of the radiator.
While you’re checking the radiator, also inspect the cap for any signs of damage or wear. A faulty radiator cap can cause the coolant to boil over and lead to engine damage.
Smell and Appearance
Finally, it’s important to use your senses to check for any signs of trouble. If you notice a sweet, fruity smell coming from the engine or see any discoloration or debris in the coolant, it could be a sign of a more serious problem. In this case, it’s best to have the vehicle inspected by a professional mechanic.
Regularly checking the coolant level and condition can help prevent costly engine damage and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Does Coolant Expire?

Coolant is an essential component in the cooling system of an engine, and it is necessary to keep the engine from overheating. However, many people are not aware of whether coolant expires or not. This section aims to answer the question of whether coolant expires and what are the signs of degradation.
Understanding Shelf Life
Coolant or antifreeze does not expire when it is still sealed in the original container. The shelf life of the coolant is indefinite as long as it remains in its original container. The expiration date is not a consideration when the coolant is still sealed and unopened.
Signs of Degradation
Coolant can degrade over time, especially if it is exposed to contaminants. The signs of degradation include a slushy or thick consistency, a bad smell, and corrosive deposits.
If the coolant appears to be thick or has debris or dirt, it is an indication that it has been contaminated. The coolant can also corrode over time, leading to the formation of corrosive deposits.
Effect of Contaminants
Contaminants can affect the shelf life of the coolant. If the coolant is exposed to air, it can absorb moisture, which can lead to the formation of corrosive deposits. The coolant can also absorb contaminants, such as dirt and debris, which can affect its effectiveness.
Impact of Age
Age can also affect the shelf life of the coolant. Coolant can expire after running a vehicle for 30,000 miles or two years (in the case of silicated coolants) and 100,000 miles or five years (in the case of extended drain coolants).
However, if the coolant is still in its original container and unopened, it can last indefinitely.
In conclusion, coolant does not expire when it is still sealed in its original container. However, it can degrade over time if it is exposed to contaminants.
The signs of degradation include a slushy or thick consistency, a bad smell, and corrosive deposits. It is essential to keep the coolant in its original container and avoid exposing it to contaminants to ensure its effectiveness.
How to Dispose of Coolant
Disposing of coolant is an important task that should be done carefully to prevent environmental contamination and harm to pets. Here are some instructions on how to dispose of coolant properly:
- Check with your local recycling center or auto parts shop to see if they accept used coolant. Many recycling centers and auto parts shops will accept used coolant and dispose of it safely.
- If there are no recycling centers or auto parts shops near you, check with your local waste management facility to see if they accept used coolant. Some waste management facilities will accept used coolant, but they may have specific instructions on how to dispose of it.
- Never pour used coolant down the drain or onto the ground. This can contaminate the soil and water supply.
- When transporting used coolant, make sure it is in a sealed container and labeled as hazardous waste.
- If you accidentally spill coolant, clean it up immediately using an absorbent material such as kitty litter or sand. Place the used absorbent material in a sealed container and dispose of it according to your local regulations.
Hey, as a mechanic, you definitely want to do the right thing when it comes to getting rid of coolant. It’s not just about your own safety, but also the environment and other folks. So, here’s the deal: follow these steps, and you’ll be tossing that coolant out the right way – safe and sound for everyone.
To Summarize
In summary, engine coolant or antifreeze does not expire in the traditional sense of the word. Unopened and properly stored coolant can last indefinitely. However, once opened and exposed to air, it can start to degrade and lose its effectiveness over time.
The shelf life of opened coolant depends on various factors such as the type of coolant, storage conditions, and whether it has been mixed with water.
Silicated coolants typically last for up to 2 years or 30,000 miles, while extended drain coolants can last for up to 5 years or 100,000 miles. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and replace the coolant at the recommended intervals to ensure optimal engine performance.
Using expired coolant can have adverse effects on the engine, including reduced cooling performance, corrosion, and clogs in the cooling system. It’s crucial to check the coolant regularly and top it off as needed to maintain the proper water/antifreeze ratio and prevent engine damage.
In conclusion, while engine coolant does not expire like food or medicine, it can degrade over time and lose its effectiveness.
It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and replace the coolant at the recommended intervals to ensure optimal engine performance and prevent costly repairs.


![Toyota Long Life Coolant and Super Long Life Coolant [Review] toyota long life coolant](https://roadsumo.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/toyota-long-life-coolant-150x150.jpg)


![Ford V10 Life Expectancy [How Many Miles Will It Last?] ford v10 life expectancy](https://roadsumo.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/ford-v10-life-expectancy-150x150.jpg)



