The fuel pump is a crucial component in a vehicle’s fuel system, responsible for delivering fuel from the gas tank to the engine. However, many car owners may not know where the fuel pump is located in their vehicle.
Typically, the fuel pump is located in the fuel tank, making it difficult to access and replace. Some vehicles may have an access port on the trunk floor or under the rear seat for easier access.
Diesel-fueled engines may have two fuel pumps, with a lift pump inside the fuel tank and a high-pressure pump at the engine.
Knowing the location of the fuel pump can be helpful for diagnosing and repairing fuel system issues. It can also be useful for routine maintenance, such as replacing a worn-out fuel pump.
In this article, we will explore where the fuel pump is located in different types of vehicles and provide tips for accessing and replacing it.
Where is the Fuel Pump Located?
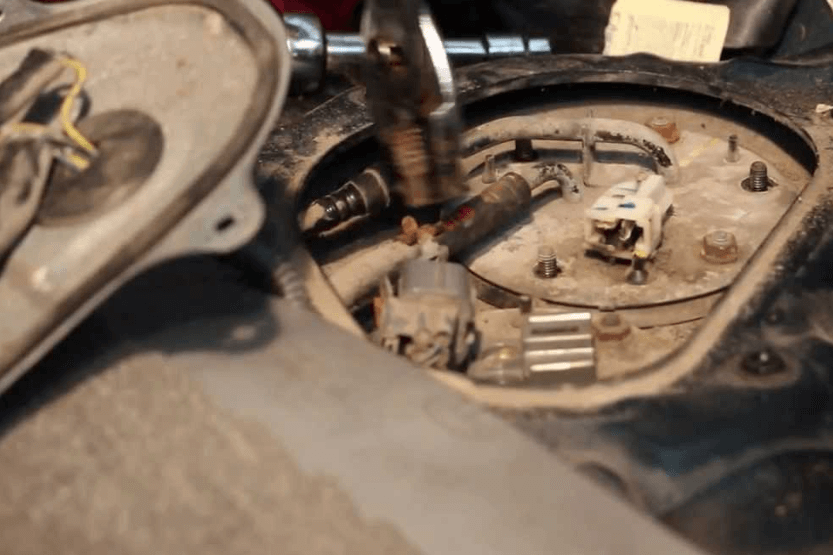
As per Capitol Chevrolet of Salem, the fuel pump is a crucial component of the fuel system that is responsible for transferring gasoline or petrol from the fuel tank to the engine.
It is typically located inside the fuel tank, although the exact location can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
Accessing the fuel pump can be difficult in some vehicles, as it may require removing the gas tank. However, some vehicles may have an access port that makes it easier to reach the fuel pump.
It is important to consult a repair manual or repair database to determine the exact location of the fuel pump in your car.
The fuel pump is responsible for maintaining the fuel pressure required for the engine to run properly. If the fuel pressure is too low, the engine may not start or may stall while driving.
On the other hand, if the fuel pressure is too high, it can cause damage to the fuel system components such as the fuel pressure regulator, fuel injector, or fuel rail.
In gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines, the fuel pump is typically a high-pressure pump that delivers fuel directly to the fuel injector. This allows for more precise control of the fuel injection process, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and performance.
In summary, the fuel pump is an essential component of the fuel system that is responsible for delivering gasoline or petrol to the engine.
It is typically located inside the fuel tank, and accessing it can be difficult in some vehicles. Proper maintenance of the fuel system, including the fuel pump, is crucial for the proper functioning of the engine.
Types of Fuel Pumps
Fuel pumps are essential components of any internal combustion engine. They are responsible for delivering fuel from the fuel tank to the engine’s combustion chamber.
According to The Engineers Post (.com), there are several types of fuel pumps available in the market today, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages.
Mechanical Fuel Pump
A mechanical fuel pump is a type of positive-displacement pump that is commonly used in older vehicles. This type of pump is driven by the engine’s camshaft and operates by creating a vacuum that draws fuel from the tank and into the carburetor.
Mechanical fuel pumps are simple, reliable, and easy to maintain. However, they can only deliver a limited amount of fuel, which makes them unsuitable for high-performance engines.
Electric Fuel Pump
Electric fuel pumps are the most common type of fuel pump used in modern vehicles. They are powered by an electric motor and are located inside the fuel tank. Electric fuel pumps are capable of delivering a high volume of fuel, making them suitable for high-performance engines.
They are also more efficient than mechanical fuel pumps and can be controlled by the engine’s computer.
Primary Fuel Pump
A primary fuel pump is a type of electric fuel pump that is located inside the fuel tank. It is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine’s secondary fuel pump, which is usually located near the engine.
Primary fuel pumps are designed to operate at low pressure and are typically less expensive than secondary fuel pumps.
Mechanical Pump
A mechanical pump is a type of fuel pump that is driven by the engine’s camshaft. It is commonly used in older vehicles and is often found in carbureted engines. Mechanical pumps are simple, reliable, and easy to maintain.
However, they can only deliver a limited amount of fuel, which makes them unsuitable for high-performance engines.
Electric Pump
An electric pump is a type of fuel pump that is powered by an electric motor. It is commonly used in modern vehicles and is located inside the fuel tank.
Electric pumps are capable of delivering a high volume of fuel, making them suitable for high-performance engines. They are also more efficient than mechanical pumps and can be controlled by the engine’s computer.
In conclusion, there are several types of fuel pumps available in the market today, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a fuel pump, it is essential to consider the engine’s performance requirements, fuel system design, and budget.
Components of a Fuel Pump

A fuel pump is a vital component of the fuel system in any liquid-fueled engine. It is responsible for transferring fuel from the fuel tank to the engine where it is mixed with air and burned to produce power.
As per Issuu (.com), a typical fuel pump consists of several components that work together to ensure the proper functioning of the fuel system.
Electric Motor
An electric motor is the primary component of an electric fuel pump. It is a small brush-type DC motor that drives the fuel pump. The electric motor is connected to the fuel pump through a shaft and rotates the pump to create pressure that moves fuel from the tank to the engine.
Pump Assembly
The fuel pump assembly is a critical component that includes the electric motor, fuel pump, and other parts such as a fuel gauge sending unit, a pressure regulator valve, a fuel tank pressure sensor, a pump intake strainer, and the main fuel system filter.
The fuel pump assembly is responsible for maintaining the proper pressure and flow of fuel to the engine.
Fuel Filter
The fuel filter is another essential component of the fuel pump. It is responsible for removing impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. The fuel filter helps to ensure the proper functioning of the engine and extends the life of the fuel system.
Plunger and Diaphragm
The plunger and diaphragm are two critical components of a mechanical fuel pump. The plunger is a cylindrical shaft that moves up and down in a bore to create pressure that moves fuel from the tank to the engine.
The diaphragm is a flexible membrane that separates the fuel from the motor oil and creates a vacuum to draw fuel from the tank.
Sender Unit and Level Sensor
The sender unit and level sensor are two components that work together to measure the amount of fuel in the tank.
The sender unit is a float that moves up and down with the fuel level and sends a signal to the level sensor. The level sensor then sends a signal to the fuel gauge to indicate the fuel level to the driver.
Reservoir and Outlet Tube
The reservoir and outlet tube are two components that work together to store and deliver fuel to the engine.
The reservoir is a container that holds a small amount of fuel to ensure that the pump always has fuel available to deliver to the engine. The outlet tube is a small pipe that delivers fuel from the pump to the engine.
In summary, a fuel pump consists of several components that work together to ensure the proper functioning of the fuel system. These components include the electric motor, pump assembly, fuel filter, plunger, diaphragm, sender unit, level sensor, reservoir, and outlet tube.
Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring that the engine receives the proper amount of fuel at the correct pressure and flow rate.
Symptoms of a Bad Fuel Pump

A failing fuel pump can cause a range of symptoms that can be frustrating and even dangerous. As per Heart Auto Care (.com), here are some of the most common symptoms of a bad fuel pump:
- Engine won’t start: The fuel pump is responsible for supplying fuel to the engine, and if it fails, the engine won’t be able to start. If you turn the key and the engine cranks but doesn’t start, the fuel pump may be the culprit.
- Stalling or misfiring: If the fuel pump is failing, it may not be able to supply enough fuel to the engine, causing it to stall or misfire. This can be especially noticeable when the engine is under load, such as when accelerating or climbing a hill.
- Loss of power: A failing fuel pump may not be able to supply enough fuel to the engine, causing a loss of power. This can make it difficult to accelerate or maintain speed.
- Engine performance issues: A bad fuel pump can cause a range of engine performance issues, including rough idling, hesitation, and surging. These symptoms can be caused by a number of different problems, but a failing fuel pump is one of the most common.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic.
A failing fuel pump can cause serious damage to your engine if left unchecked, and it’s not a problem that you should try to fix on your own unless you have the necessary skills and experience.
Testing the Fuel Pump
When experiencing issues with a vehicle’s fuel system, the fuel pump is often the first component to be checked. Testing the fuel pump can be done in a number of ways, including a pressure test and a voltage test.
Pressure Test
A pressure test is one of the most common methods used to test the fuel pump. This test involves connecting a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail or fuel line to measure the pressure of the fuel system.
The fuel pressure gauge should be connected to the test port on the fuel rail or fuel line, which can be located in the engine compartment or under the vehicle.
Once the gauge is connected, the vehicle’s ignition should be turned on, but the engine should not be started.
The fuel pressure gauge should then be observed to see if the fuel pressure is within the manufacturer’s specifications. If the fuel pressure is not within the specified range, it may indicate a problem with the fuel pump or fuel system.
Voltage Test
Another method to test the fuel pump is a voltage test. This test involves using a multimeter to measure the voltage at the fuel pump connector. The fuel pump connector can be located near the fuel tank or in the engine compartment.
To perform the voltage test, the vehicle’s ignition should be turned on, but the engine should not be started. The multimeter should then be set to measure DC voltage and the positive and negative leads should be connected to the fuel pump connector.
The multimeter should then be observed to see if the voltage is within the manufacturer’s specifications. If the voltage is not within the specified range, it may indicate a problem with the fuel pump or the wiring to the fuel pump.
It is important to note that testing the fuel pump should only be done by a qualified technician with the necessary tools and equipment. If an issue is found with the fuel pump during testing, it is recommended to have it replaced by a professional to ensure proper installation and operation.
Fuel Pump Replacement

Replacing a fuel pump can be a complex and time-consuming process, but it is necessary if your vehicle is experiencing fuel delivery issues. It is recommended to consult a repair manual for your specific make and model before attempting to replace the fuel pump.
The fuel pump is typically located inside the fuel tank, which means the tank must be removed in order to access and replace the pump. This can be a difficult and messy process, so it is important to take proper safety precautions and have the necessary tools and equipment on hand.
Before replacing the fuel pump, it is important to diagnose the issue to ensure that the pump is the root cause of the problem. Other components, such as the fuel filter or catalytic converter, may also be contributing to the issue.
Once the fuel pump has been replaced, it is important to test the system to ensure proper functionality. This may involve running the vehicle and checking for leaks or abnormal noises.
As a mechanic, I can tell you that replacing a fuel pump is no simple task. It’s a complex process that demands careful planning, the right tools, and in-depth knowledge. Safety should be your top priority, so always take the necessary precautions.
Before diving in, it’s a smart move to consult a repair manual specific to your vehicle. This will provide you with detailed instructions tailored to your car’s make and model, helping you avoid costly mistakes and ensuring a successful fuel pump replacement.
Key Takeaways
The fuel pump is vital, delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. It’s either inside the tank or outside, location varies by vehicle. Inside-tank pumps are accessed via trunk or under the rear seat. Outside-tank ones are near the engine or along the frame rail.
Look for signs of trouble: stalling, whining noises, sputtering, or decreased performance. It can also cause surging, misfiring, a Check Engine Light, worn spark plug tips, and low fuel pressure.
Suspect a fuel pump issue? Have it checked by a mechanic. Replacement costs $200 to $1,250, depending on the vehicle. Usually takes a couple of hours, with most cost in the part, especially if it’s a full module assembly.
Understanding the fuel pump’s role is vital for a healthy fuel system. Stay alert to symptoms and get it fixed by a mechanic to keep your vehicle running smoothly and safely.


![Transmission Fluid Pump [10 Best Pumps] transmission fluid pump](https://roadsumo.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/transmission-fluid-pump-150x150.jpg)


![Best Fuel Stabilizer [10 Top Stabilizers] best fuel stabilizer](https://roadsumo.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/best-fuel-stabilizer-150x150.jpg)


